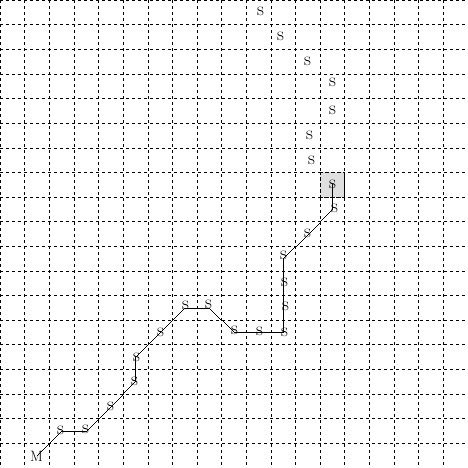

The figure above shows the location of stream elements (denoted by "S") and an arbitrary stream element shaded in grey. Water collecting in the stream element by means of rainfall, base flow, saturated area runoff, or infiltration excess will be routed to the mouth of the stream, which is denoted by "M" in the figure above.
The change in elevation $\Delta h$ between the given stream element and the stream mouth is calculated. The average slope of the path calculated using this change in elevation and the length $d$ of the stream path is $\frac{\Delta h}{d}$. A parametric quantity representing the stream channel routing velocity $V_{ch}$ for a tangent slope of one is specified. Then, the time required to reach the stream mouth is given as
time = $\frac{d^2}{\Delta h V_{ch}}.$