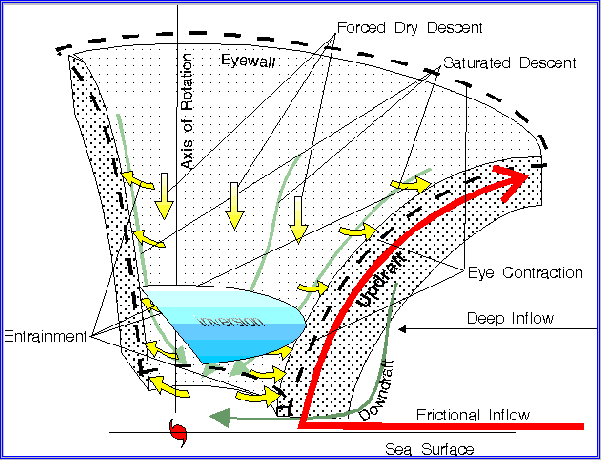
Schematic illustration of the secondary flow around the eye of a hurricane.
-
The frictional indraft feeds the buoyancy-driven primary updraft and outflow in the eyewall cloud. (red)
-
Saturated convective downdrafts in the eyewall (green) and the evaporationally driven descent along the inner edge of the eyewall (green) feed moist air into the volume below the inversion surface.
-
Dynamically driven descent (yellow) of dry air inside the eye warms the air column adiabatically. The descent is forced as entrainment into the eyewall draws mass from the bottom of the eye into the eyewall. Balance between moist-air production and loss by entrainment determines the rate of rise or fall of the inversion.
Formation of the Hurricane Eye
Jonathan Vigh, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado
Tropical cyclones are often observed to rapidly intensify with a concomitant increase in structural organization during or just after the formation of a central region characterized by lighter winds and little precipitation known as the hurricane 'eye'. Formation of the eye apparently occurs due to the juxtaposition of two structural trends in the developing storm vortex: convection begins to concentrate at some preferred radial distance from the storm center while a region of subsiding air develops within the emerging convective annulus.
Various mechanisms have been proffered to explain why and how these structural changes occur. These may be grossly classified into several categories:
-
kinematic or thermodynamic aspects of the intensifying storm act to force subsidence in the center,
-
boundary layer frictional processes and/or geometric considerations lead to a preferred radius of upward motion and convective forcing, and
-
changes occur in the storm's convective morphology, such as an encircling rain band, which also drive central subsidence.
Indeed, eye formation may result as a consequence of all of these (and possibly other) mechanisms acting in concert. This work examines the relative importance of each of the various mechanisms with the goal of determining whether there is a unique dynamical pathway to tropical cyclone eye formation.

